Trading CFDs on Stocks vs ETFs: Differences and AdvantagesTrading CFDs on Stocks vs ETFs: Differences and Advantages
Many traders wonder whether it’s worth trading ETFs vs stocks. The truth is that they both offer distinct advantages depending on your strategy. Whether you're drawn to the diversification of ETFs or the high volatility of individual stocks, understanding their differences is key. This article breaks down the difference between stocks and ETFs and the advantages of each.
What Are ETFs vs Stocks?
Although you are well aware of what stocks and ETFs are, let us give a quick overview. ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, are collections of assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities bundled into a single security. Instead of buying individual assets, traders gain exposure to an entire market segment or strategy by trading ETFs. For example, SPY tracks the S&P 500, providing access to 500 major companies in one trade. ETFs are traded on exchanges like stocks, with prices fluctuating throughout the day based on supply and demand.
Stocks, by contrast, signify direct ownership in a particular company. When trading stocks, you’re focusing on the performance of that single entity, whether it’s a household name like Tesla (TSLA) or an emerging small-cap company. In comparing stocks vs an ETF, stocks are often more volatile than ETFs, creating opportunities for traders to capture sharp price movements.
In this article, we will talk about CFDs on ETFs and stocks. Contracts for Difference (CFDs) allow traders to speculate on the rising and falling prices of an asset without owning it. To explore a world of stocks and ETFs, head over to FXOpen.
Key Differences Between ETFs and Stocks
Understanding the distinctions between an ETF vs stocks is essential for traders aiming to refine their strategies. While both are popular instruments, they behave differently in the market and suit different trading approaches. Let’s break it down.
1. Composition
The primary difference between an ETF and a stock is its makeup. ETFs are baskets of assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities, offering built-in diversification. For example, the Invesco QQQ ETF holds top Nasdaq-listed companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Tesla. Stocks, however, represent a single company. Trading a stock like Amazon (AMZN) means your potential returns depend solely on its performance, while ETFs spread risk across multiple assets.
2. Volatility
Stocks are generally more volatile. A single earnings miss or CEO resignation can send a stock’s price soaring or crashing. ETFs, because they pool multiple assets, experience smaller swings. For instance, SPY’s price tends to move more steadily than a volatile stock like Tesla, making ETFs potentially easier to analyse for certain trading strategies.
3. Liquidity and Trading Volume
Liquidity varies significantly. ETFs tracking major indices like SPY are considered liquid instruments, with high trading volumes. Stocks can be just as liquid, especially large-cap companies, but smaller or niche ETFs and stocks may suffer from lower liquidity and wider spreads or gaps in pricing.
4. Costs
Investing in stocks typically involves just the price of the shares and brokerage fees. ETFs often have expense ratios—annual fees taken from the fund’s value. While these are usually small (e.g., 0.09% for SPY), they’re an added cost traders need to consider.
However, with ETF CFDs, these fees are bypassed, leaving traders with only the broker’s spread and commission to consider. Stock CFDs work similarly, eliminating transaction costs tied to owning the underlying asset.
Advantages of Trading ETFs
Trading ETFs offers unique opportunities that appeal to a range of strategies. Their structure, diversity, and flexibility make them a valuable choice for traders. Here’s what sets them apart:
1. Diversification in a Single Trade
Trading ETFs gives exposure to a group of assets, reducing the risk of being impacted by a single asset's performance. For instance, SPY tracks the S&P 500, spreading risk across 500 companies. This makes ETFs a great way to trade entire sectors or indices without committing to individual assets.
2. Sector or Thematic Focus
ETFs allow traders to target industries, regions, or themes with precision. Whether it's technology through XLK, emerging markets via EEM, or even volatility with UVXY, ETFs open the door to strategies that align with traders’ interests and market views.
3. Lower Volatility
Because ETFs pool assets, they experience less extreme price movements than individual stocks. This steadier behaviour can make them suitable for traders looking to avoid the sharp volatility of single stocks while still taking advantage of price action.
4. Liquidity in Major Funds
Popular ETFs like QQQ and SPY are highly liquid, which may contribute to tighter spreads. Their volume also supports smooth execution for both large and small positions.
5. Accessibility Through CFDs
Many traders prefer ETFs via CFDs, which allow traders to open buy and sell positions without owning the underlying asset. CFDs often provide leverage, giving traders the potential to amplify returns while keeping costs tied to spreads and commissions instead of fund expense ratios (please remember about high risks related to leverage trading).
Advantages of Trading Stocks
Trading stocks offers a direct and focused way to engage with the market. In ETF trading vs stocks, stocks may provide unique opportunities for traders who are drawn to fast-paced action or want to specialise in specific companies or sectors. Here’s what makes trading stocks appealing:
1. High Volatility for Bigger Moves
Stocks often experience significant price swings, creating potential opportunities for traders to capitalise on sharp movements. For example, earnings reports, product launches, or market news can drive stocks like Tesla (TSLA) or Amazon (AMZN) to see dramatic intraday price changes.
2. Targeted Exposure
With stocks, traders can zero in on a single company, sector, or niche. If a trader believes Apple (AAPL) is set to gain due to new product developments, they can focus entirely on that potential without being diluted by other assets in a fund.
3. News Sensitivity
Stocks respond quickly and significantly to news events, providing frequent trading setups. Mergers, management changes, or regulatory updates often result in immediate price movements, making them popular among traders who thrive on analysing market catalysts.
4. Wide Range of Opportunities
The sheer variety of stocks—from large-cap giants to small-cap companies—offers endless opportunities for traders. Whether trading high-profile names like Nvidia (NVDA) or speculative small-caps, there’s something for every trading style and risk tolerance.
5. Leverage with CFDs
Stocks can also be traded via CFDs, allowing traders to take advantage of price movements with smaller initial capital. This opens the door to flexible position sizes and leverage, amplifying potential returns in active trading.
ETFs for Swing Trade and Day Trade
ETFs cater to both swing and day traders with their diverse offerings and high liquidity. Some popular swing trading ETFs and ETFs for day trading strategies include:
ETFs for Swing Trading
- SPY (S&P 500 ETF): Tracks the S&P 500, offering exposure to large-cap US companies with steady trends.
- IWO (Russell 2000 ETF): Focuses on small-cap stocks, which tend to be more volatile, providing swing traders with stronger price movements.
- XLK (Technology Select Sector SPDR): A tech-heavy ETF that moves in response to sector trends, popular for capturing medium-term shifts.
- XLE (Energy Select Sector SPDR): Tracks energy companies, useful for swing traders analysing oil and energy market fluctuations.
Day Trading ETFs:
- QQQ (Invesco Nasdaq-100 ETF): Offers high intraday liquidity and volatility, making it a favourite for fast trades in tech-heavy markets.
- UVXY (ProShares Ultra VIX Short-Term Futures ETF): A volatility ETF that reacts quickly to market fear, providing potential opportunities for rapid price changes.
- XLF (Financial Select Sector SPDR): Tracks financial stocks and has consistent volume for capturing short-term sector-driven moves.
Stocks for Swing Trading and Day Trading
Selecting the right stocks is crucial for effective trading. High liquidity and volatility are key factors that make certain stocks more suitable for swing and day trading. Here are some of the most popular options for both styles:
Stocks for Swing Trading
- Apple Inc. (AAPL): Known for its consistent performance and clear trends.
- Tesla Inc. (TSLA): Exhibits significant price movements, offering potential opportunities to capitalise on medium-term swings.
- NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA): A leader in the semiconductor industry with strong momentum, suitable for capturing sector trends.
- Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN): Provides steady price action, allowing traders to take advantage of consistent movements.
Stocks for Day Trading
- Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD): High daily volume and volatility make it a favourite among day traders.
- Meta Platforms Inc. (META): Offers substantial intraday price swings, presenting potential trading opportunities.
- Microsoft Corporation (MSFT): Combines liquidity with moderate volatility, suitable for quick trades.
- Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL): Provides consistent intraday movements.
How to Choose Between an ETF vs Individual Stocks for Trading
Choosing between stocks and ETFs depends on your trading goals, strategy, and risk appetite. Each offers unique advantages, so understanding their characteristics can help you decide which suits your approach.
- Risk Tolerance: Stocks often come with higher volatility, making them attractive for traders comfortable with sharper price movements. ETFs offer diversification, which can reduce the impact of individual market shocks.
- Trading Strategy: For short-term trades, highly liquid ETFs like QQQ or volatile stocks like TSLA might be considerable. If you're swing trading, ETFs and large-cap stocks may provide steady trends.
- Market Focus: In individual stocks vs ETFs, ETFs give access to broad sectors or indices, popular among traders analysing macro trends. Stocks allow for focused plays on individual companies reacting to earnings or news.
- Time Commitment: Stocks typically require more monitoring due to their rapid price changes. ETFs, especially sector-specific ones, may demand less frequent attention depending on your strategy.
The Bottom Line
ETFs and stocks may offer unique opportunities, whether you're targeting diversification or sharp price movements. By understanding the differences between ETFs versus stocks and aligning them with your strategy, you can take advantage of different trading conditions. Ready to start trading? Open an FXOpen account today to access a wide range of ETF and stock CFDs with trading conditions designed for active traders.
FAQ
What Is an ETF vs a Stock?
ETFs (exchange-traded funds) are collections of assets, such as stocks or bonds, combined into a single tradable unit. They offer built-in diversification, as buying one ETF provides exposure to multiple assets. Stocks, in contrast, signify ownership in an individual company.
Should I Trade the S&P 500 or Individual Stocks?
Trading the S&P 500 (via ETFs like SPY or through index CFDs) provides exposure to the 500 largest US companies, reducing reliance on any single stock. Individual stocks offer higher volatility and opportunities for sharper price movements. Evaluate your strategy and risk tolerance to choose the suitable asset.
ETFs vs Individual Stocks: Which Is Better?
Neither ETFs nor individual stocks are inherently better—it depends on your goals. ETFs offer diversification and potentially lower volatility, making them suitable for broad market exposure. Stocks provide targeted opportunities from individual company performance.
Do ETFs Pay Dividends?
Yes, ETFs often pay dividends when their underlying holdings generate income. These are typically paid out periodically, similar to dividends from individual stocks. However, when trading CFDs, dividends are not paid in the traditional sense, as you do not own the underlying asset. However, adjustments are made to your account to reflect dividend payments.
Can I Sell ETFs Anytime?
ETFs trade on exchanges during market hours, making them highly liquid. Therefore, you can buy or sell ETFs on specific days and hours.
Trade on TradingView with FXOpen. Consider opening an account and access over 700 markets with tight spreads from 0.0 pips and low commissions from $1.50 per lot.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Cfdtrading
How to Use Stock Volume in CFD TradingHow to Use Stock Volume in CFD Trading
Volume is one of the fundamental aspects of all markets. If you're wondering, "What does volume mean in the stock market?," you're about to discover how this critical measure of shares traded can unlock deeper insights into market trends and investor behaviour. We delve into how to use stock volume to improve your trading, offering practical approaches for confirming market sentiment, trends, reversals, and more.
What Is Volume in the Stock Market?
The volume in the stock market definition refers to the total number of shares traded during a specific time frame. It's a vital indicator of market activity and investor interest in a particular stock.
High volume often signals strong investor interest and market movement, either upward or downward. Conversely, low volume may indicate decreased interest or uncertainty in a stock. In essence, it provides insights into sentiment, helps confirm trends, and aids in identifying potential reversals or breakouts.
As we walk through the varying insights volume offers stock traders, you may gain the best understanding by applying your knowledge to real-time charts. Head over to FXOpen’s free TickTrader platform to see how volume affects hundreds of unique stocks.
Volume and Market Sentiment
When considering volume in a stock, meaning its traded shares, its relationship with market sentiment becomes pivotal. This sentiment, essentially the collective attitude of traders towards a stock, is often inferred from volume patterns.
At its most basic, high trading activity during a stock's price increase is often seen as a confirmation of positive sentiment, showing trader confidence. Such a scenario often reflects a robust demand overpowering supply.
In contrast, if a stock declines on high volume, this may signal negative sentiment, suggesting a strong selling pressure. This situation typically indicates that investors and traders are actively offloading their shares.
Volume and Price Movement
So, how does volume affect stock prices? Volume acts as a force behind price movements, as discussed.
However, its impact isn't always straightforward. A stock might rise on low volume, which can be a sign of caution, as it may indicate a lack of conviction among traders, potentially making the price rise unsustainable. Similarly, a drop on low volume might not necessarily signify a bearish trend but rather a temporary lack of interest.
Additionally, the number of shares traded can be crucial in identifying a stock’s tops or bottoms. For instance, a sudden spike after a long period of price increase might signal a top, as it could represent a final push by exhausted buyers before a reversal. Similarly, a significant increase in market activity at a low could indicate a bottom.
Identifying Trading Signals with Volume
Learning how to trade volume involves recognising nuanced trading signals that volume fluctuations can offer. Beyond the basic interpretations of high or low volume, traders look for specific patterns or anomalies in activity data to make informed decisions.
One key signal is the volume spike. A sudden increase in trading activity, especially when it deviates notably from the norm, may indicate a significant event or sentiment change. For instance, a volume spike accompanying a breakout from a consolidation pattern might confirm the strength of a new trend, offering a buying opportunity for traders.
Conversely, an unexpected, sustained drop in interest during a steady trend might be a warning sign. This could suggest that the current trend is losing momentum and might be nearing its end, reflecting a potential exit point or even a reversal opportunity.
Another aspect to consider is the trend over time. Gradually increasing volume in a trending market reinforces the trend's validity and vice versa.
Overall, trading volume isn't just about high or low numbers. It's about understanding the context of these changes and how they align with price movements.
Volume Indicators and Tools
When exploring how to use volume in trading, several key indicators and tools stand out. These provide insights into market dynamics, aiding in decision-making:
- On Balance Volume (OBV): OBV totals volume during up periods and subtracts it during down periods. A rising OBV usually suggests bullish trends, while a falling OBV indicates bearish trends. It's used to confirm movements or spot divergences.
- Volume Price Trend (VPT): VPT combines volume and price change to assess the strength of price moves. An increasing VPT usually indicates strong buying pressure, while a decreasing VPT suggests selling pressure.
- Accumulation/Distribution Line: This indicator considers the trading range and the volume. It helps identify whether a stock is being accumulated (bought) or distributed (sold). A rising line usually suggests accumulation, while a falling line indicates distribution.
- Chaikin Money Flow (CMF): CMF combines price and volume to measure buying and selling pressure over a set period. A positive CMF usually demonstrates buying interest, while a negative CMF suggests that sellers are in charge.
Volume as an Indicator of Liquidity
Lastly, volume is a key indicator of liquidity in the stock market. High trading activity reflects that a significant number of shares are being bought and sold, which typically indicates good liquidity. This liquidity may help traders execute trades quickly and at prices close to the market rates, reducing the cost of transactions.
Conversely, low volume signals poor liquidity, where fewer shares are traded. In such scenarios, executing large orders may be challenging without significantly impacting the stock. Such a lack of liquidity can lead to larger bid-ask spreads and potentially less favourable execution prices for traders.
The Bottom Line
As we've journeyed through the intricate world of stock volume, it's clear that understanding volume is more than a skill – it's an essential aspect of savvy trading. From recognising sentiment to navigating various market conditions, volume serves as a powerful tool in your trading arsenal.
To put this knowledge into practice and experience the dynamic world of trading, consider opening an FXOpen account. Once you do, you'll have the opportunity to apply these insights in real-time, potentially enhancing your trading journey with informed decisions driven by volume analysis. Happy trading!
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Mastering CFD Trading: A Comprehensive Beginner's GuideContracts for Difference (CFDs) have garnered significant attention as derivative products that offer traders the ability to speculate on the price movements of various assets without the need to own them physically. These financial instruments emerged in the latter part of the 20th century, propelled by the advent of the internet revolution, which revolutionized trading by facilitating swift and convenient short-term transactions.
CFDs have since become an integral part of the repertoire offered by prominent brokers, providing traders with enhanced leverage and access to an extensive range of markets that encompass stocks, indices, currencies, and commodities. This broad market coverage has contributed to the popularity and widespread adoption of CFDs among traders seeking diverse investment opportunities.
The historical roots of CFDs can be traced back to the late 1980s and early 1990s. It was during this period that derivative trading witnessed significant advancements, driven by technological progress and regulatory changes. The introduction of electronic trading platforms and the availability of real-time market data allowed traders to execute trades swiftly and efficiently, leading to the development of CFDs as a viable financial instrument.
The operational mechanics of CFDs are relatively straightforward. When trading a CFD, the trader enters into a contract with a broker, mirroring the price movements of the underlying asset. This contract stipulates that the trader will pay or receive the difference in price between the opening and closing positions of the CFD. If the price of the underlying asset moves in the trader's favor, they stand to make a profit. Conversely, if the price moves against their position, they may incur a loss.
One of the key advantages of trading CFDs is the ability to utilize leverage. Leverage allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller initial investment. This amplifies potential gains, but it is important to note that it also magnifies potential losses. Traders should exercise caution and employ risk management strategies when using leverage in CFD trading.
Furthermore, CFDs offer traders the flexibility to profit from both rising and falling markets. Through a process known as short-selling, traders can speculate on price declines and potentially profit from downward market movements. This ability to take both long and short positions provides traders with opportunities to capitalize on market trends and volatility.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge that CFD trading carries inherent risks. Due to the leverage involved, losses can exceed the initial investment, potentially resulting in significant financial losses. Moreover, CFD trading is subject to market volatility, and sudden price movements can lead to rapid and substantial losses.
Throughout this comprehensive article , we shall delve into the historical backdrop of CFDs, elucidate their operational mechanics, and present an evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages associated with trading these financial instruments.
History Of CFD:
Towards the conclusion of the 20th century, the landscape of exchange trading underwent a profound transformation, thanks to the advent of the Internet. This revolutionary technology empowered traders to engage in rapid short-term trades with unparalleled ease. Consequently, intraday trading emerged as a prominent trend, and astute brokers swiftly recognized the burgeoning demand for this segment among individual traders.
However, a significant predicament persisted within the trading realm - exchanges were highly specialized and compartmentalized. Currency exchanges, stock exchanges, and futures exchanges operated as distinct entities, precluding traders from capitalizing on opportunities across multiple asset classes. For instance, a trader operating with a currency broker lacked the means to profit from futures or stocks.
While opening multiple accounts with different companies was a possible solution, it was far from optimal. Furthermore, another obstacle loomed large: high leverage was imperative for generating profits through short-term transactions, yet traditional stock exchanges were averse to the risks associated with margin trading.
In response to these challenges, visionaries at UBS Investment Bank conceptualized a new trading instrument known as the contract for difference (CFD). This innovative derivative allowed traders to profit from the price fluctuations of various assets without the need to physically own them or conduct transactions on the underlying exchanges. Traders could now conveniently engage in trading shares, oil, and other commodities using a single broker. Additionally, CFDs provided the desired leverage for short-term trading, overcoming the limitations imposed by traditional stock exchanges.
Over time, CFDs became widely available, offered by popular brokers operating in diverse markets, including the forex market. Presently, this versatile financial instrument is successfully utilized by both short-term traders and long-term investors, catering to a broad spectrum of trading styles and planning horizons. The flexibility and accessibility of CFDs have made them an indispensable tool in the arsenal of market participants seeking to capitalize on price movements and maximize their trading potential.
CFD Leverage Explained:
One of the notable features of CFD trading is the availability of margin trading, which enables traders to borrow funds from their brokers. This concept is closely tied to the notion of leverage, which has a significant impact on the trading process. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions in the market with a smaller amount of their own capital.
To illustrate the concept, let's consider an example. Suppose a trader utilizes a 1:50 leverage. This means that with just $1,000 of their own funds, they can open a position equivalent to $50,000. In this scenario, the borrowed funds provided by the broker amplify the trader's purchasing power, enabling them to access larger market positions.
The level of leverage available in CFD trading varies depending on the underlying asset being traded. For instance, when trading shares, the leverage typically ranges up to 1:20. On the other hand, for commodities like oil, leverage can often reach as high as 1:100.
It is important to note that when comparing leverage in CFD trading to leverage in forex currency pairs, the ratios may appear different. A 1:20 leverage in CFDs might seem relatively lower when contrasted with the leverage commonly available in forex trading. However, it is crucial to consider these ratios within the context of their respective markets.
In traditional stock markets, equity leverage is typically limited and rarely exceeds 1:2. This means that traders in those markets have less flexibility in terms of controlling larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. In contrast, CFDs provide traders with significantly higher leverage, allowing them to amplify their potential gains and losses.
It is important to approach leverage in CFD trading with caution and exercise risk management strategies. While leverage can magnify profits, it also amplifies potential losses. Traders should be mindful of the increased risk associated with higher leverage levels and consider their risk tolerance and trading strategies accordingly.
Comparing leverage ratios across different markets provides insights into the varying degrees of flexibility and risk exposure available to traders. Understanding and utilizing leverage effectively is an essential aspect of CFD trading, enabling traders to optimize their trading strategies and potentially enhance their profitability, while remaining cognizant of the associated risks.
How CFDs Work:
Let's break down the scenario provided to understand the implications of trading CFDs compared to traditional stock ownership.
Assuming the Ask price per share is $171.23, a trader purchasing 100 shares would need to consider additional costs such as commissions and fees. In a traditional brokerage account with a 50% credit on margin, this transaction would require a minimum of $1,263 in available funds.
However, with CFD brokers, the margin requirements are typically much lower. In the past, a 5% margin was common, which would amount to $126.30 for this trade.
When opening a CFD position, the trader will immediately experience a loss equal to the size of the spread at the time of the trade. For example, if the spread is 5 cents, the stock price must rise by 5 cents for the position to reach the breakeven level.
If the trader owned the stock directly, they would make a 5 cents profit. However, it's important to consider that owning the stock directly would entail paying a commission, resulting in higher overall costs.
Now, let's consider the scenario where the offer price of the stock reaches $25.76. In a traditional brokerage account, positions could be closed at a profit of $50, resulting in a 3.95% return on the initial investment of $1,263.
However, in the case of CFDs, when the price reaches the same level on the national exchange, the bid price on the CFD may be slightly lower, let's say $25.74. Consequently, the profit from trading CFDs would be lower since the trader must exit the trade at the bid price. Additionally, the spread in CFD trading is typically wider compared to regular markets.
In this example, the CFD trader would earn approximately $48, resulting in a 38% return on the initial investment of $126.30.
It's worth noting that these figures are specific to the example provided and may vary depending on various factors, including the specific brokerage, market conditions, and the pricing dynamics of the underlying asset.
Why Trade CFDs / Pros And Cons Of Trading CFDs
Indeed, one of the significant advantages of trading CFDs is the expanded range of tradable instruments compared to the classical forex market. While the forex market primarily deals with currencies, CFDs provide traders with the opportunity to trade a wide array of assets. Most brokers now offer CFDs on various instruments such as gold, stocks, and stock indices, greatly diversifying the available trading opportunities.
However, it is important to note that CFDs are not a direct replacement for the underlying assets. Although the price of a CFD contract reflects the price movements of the underlying instrument, there may be differences in the actual returns. These differences can be attributed to factors such as spreads, commissions, and other costs associated with CFD trading.
Speaking of commissions, it is crucial to consider that CFD commissions may differ from those applied to the underlying asset. This distinction becomes particularly relevant in longer-term trading scenarios. Traders need to carefully evaluate the commission structure and any associated fees when assessing the overall costs of trading CFDs.
Now let's delve into the main advantages and disadvantages of trading CFDs:
Pros of CFD Trading:
1 ) Expanded Market Access: CFDs provide access to a wide range of markets, including stocks, commodities, indices, and more, allowing traders to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on various asset classes.
2 ) Leverage and Margin Trading: CFDs offer the potential for higher leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. This amplifies potential profits (as well as losses) and can enhance trading opportunities.
3 ) Ability to Profit from Both Rising and Falling Markets: CFDs enable traders to take advantage of both upward and downward price movements. Through short-selling, traders can speculate on price declines and potentially profit from falling markets.
Cons of CFD Trading:
1 ) Counterparty Risk: When trading CFDs, traders are exposed to counterparty risk, as they enter into contracts with the broker rather than owning the underlying assets. If the broker encounters financial difficulties or fails, it can impact the trader's positions and funds.
2 ) Potential for Higher Costs: CFD trading may involve additional costs such as spreads, commissions, and overnight financing charges. These costs can impact overall profitability, especially for longer-term trades.
3 ) Market Volatility and Risk: CFDs are subject to market volatility, and sudden price movements can result in rapid and substantial losses. The use of leverage in CFD trading can amplify both gains and losses, making risk management crucial.
It is essential for traders to consider these pros and cons when deciding to engage in CFD trading. Adequate risk management strategies and a thorough understanding of the underlying markets and associated costs are essential for successful and informed trading decisions.
Risks Of Trading CFDs:
Trading CFDs (Contracts for Difference) involves inherent risks that traders should be aware of before engaging in such activities. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed decisions and implementing appropriate risk management strategies. Here are some of the key risks associated with CFD trading:
Leverage Risk: CFDs allow traders to access larger market positions with a smaller initial investment. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies losses. Traders need to be cautious and manage leverage effectively to avoid significant financial setbacks.
Market Risk: CFDs are directly linked to the price movements of underlying assets, which can be influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, news events, and market sentiment. Rapid price fluctuations can lead to substantial losses, especially if positions are not managed appropriately.
Counterparty Risk: When trading CFDs, traders enter into a contractual agreement with the CFD provider. This exposes them to counterparty risk, which refers to the possibility of the provider failing to fulfill its obligations. It is crucial to choose a reputable and regulated CFD provider to minimize this risk.
Operational Risk: CFD trading platforms can experience technical issues, such as system outages or errors, which may prevent traders from executing trades or managing positions effectively. Traders should be prepared for such operational risks and have contingency plans in place.
Liquidity Risk: In certain cases, CFD markets may lack sufficient liquidity, meaning there is a limited number of buyers and sellers. This can make it challenging to enter or exit positions at desired prices, particularly during volatile market conditions. Traders should be cautious when trading illiquid CFD markets.
Hidden Costs: Some CFD brokers may impose additional fees and charges, such as overnight financing fees or spread mark-ups. These hidden costs can reduce profitability over time, and traders should carefully review the fee structure of their chosen CFD provider.
To mitigate these risks, traders are advised to implement risk management techniques, including setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, conducting thorough market analysis, and continuously monitoring positions. It is also crucial to conduct due diligence when selecting a CFD provider, ensuring they are regulated and offer transparent pricing structures and reliable customer support.
By understanding and effectively managing these risks, traders can enhance their chances of success and navigate the complexities of CFD trading more confidently.
Choosing A Broker For CFD Trading:
When selecting a broker for CFD trading, certain parameters take precedence. These include:
1 ) Reliability and Reputation: When it comes to CFD trading, the importance of a broker's reliability and reputation cannot be overstated. Given the instrument's relative lack of popularity, there may be instances of limited liquidity, which increases the temptation for unethical practices such as manipulating charts or altering quotes. It is crucial to choose a broker known for their trustworthiness and positive reputation.
2 ) Variety of CFDs for Trading: It is advisable to thoroughly examine the broker's website and review the comprehensive list of available contracts. Ensure that the list includes the specific CFDs you intend to trade. Having access to a wide range of CFD options allows you to diversify your portfolio and pursue various trading opportunities.
3 ) Contract Specifications: Identify the CFDs in the broker's list that you plan to trade frequently. Pay attention to the contract specifications, including spreads, commissions, and swaps, as they should align with your trading style and objectives. If you require high leverage, verify the leverage availability for each CFD category.
By carefully considering these parameters, you can make an informed decision when choosing a broker for CFD trading. This will contribute to a more satisfactory trading experience and help you align your trading strategy with your goals.
Conclusion:
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) provide traders with a gateway to a diverse range of popular exchange-traded assets. Through a single CFD broker, traders can engage in trading activities involving stocks, indices, and even cryptocurrencies.
The key to achieving success in CFD trading lies in the trader's level of proficiency in understanding the intricacies of specific instruments. The most favorable outcomes are typically attained by individuals who concentrate their efforts on a particular asset class or even a specific instrument within that class. By acquiring comprehensive knowledge and a deep understanding of the various factors that influence prices, traders can surpass market performance and reap the rewards they rightfully deserve. This focused approach enhances their ability to make informed decisions, seize profitable opportunities, and maximize their potential gains in the CFD market.
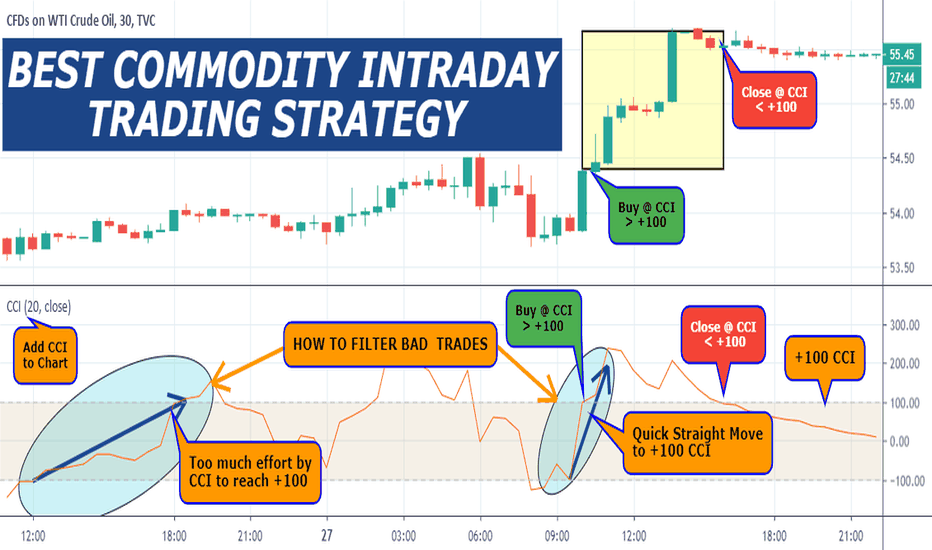
BEST COMMODITY INTRADAY TRADING STRATEGY Before we outline the best commodity intraday trading strategy, it’s important to understand that trading commodities are different from trading Forex or stocks. Every financial asset has its own set of unique characteristics. The commodity market has its own behavior, that’s why some strategies are more suitable than others to generate profits from commodity trading.
We’re going to reveal some of the most well-kept commodity trading secrets only known by successful commodity traders.
Let’s now see what commodity trading strategy you can use to buy and sell products in the commodity market.
Here is the link to "Best Commodity Intraday Trading Strategy" pdf.
tradingstrategyguides.com
My main strategy is called 'cycle-trading' a unique concept. My main strategy is called 'cycle-trading'. After years of learning and practicing after I bought a teaching-package from a visionair, I found a way of how to trade successful with CFD's on the stock-market. Every stock is following an certain cycle which repeats itself. So, movements are often appearing in the same percentage, aswel long as short. This cycles appear at all levels; when you analyse the chart at 1 month, 1 week, 1 day, 1 hour. (others I don't use). This is the case, because all in life is build by the fibonacci sequence. When you analyse the chart, you'll also see the stock market is behaving itself as the fibonacci sequence. But, still the most difficult part and what it's all about, is where does a long or a short start? and which point is telling you that the cycle is started, so that you know it will probably go to the next fibonacci resistance? .... therefore I have developed some own indicators!
The exact positions of where to open, to close and the stop loss position and take profit position is very important to be successful with trading!
My strategy is to never trade on volatile markets. You will lose your money when you do! Trade on technical-chart analysis! not on news and volatility!
One of my other strategies is that trades are only interesting and ‘safe’ to open when: you can possibly lose 1/3rd of the possible profit. So; when you set the indicators after analysing resistances, and you can lose 100 but win 300, it is worth the try!
How do I decide to open a position or not? First I analyse:
- sentiment on the market > are people in buy mode or short mode
- I have some own created indicators, some I show in my charts. Therefor I use the fibonacci sequence. My indicators tell to open a position or not and in combination with other own created indicators I decide where to place the stop loss and take profit positions.
- and this own indicators tell me when probably a new long position starts or a new short > these are the positions where I place my orders! or open directly.
- and again other own created indicators tell me how far long or short it probably goes. The take profit and stop loss positions are other positions than the resistances in the market!
- the moving-averages and bollinger-bands are very important indicators also. They are helping a lot! by making decisions.
And that is Why I win more than I lose in the end. Patience is everything, we’ll wait for the right moment! But don't forget; trading means investing. Sometimes you lose more than you win in the beginning of a period!
Most of the times the sentiment changes on Monday! please consider that when you start a position on Monday. Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday are on steady markets normally calm trading days. Than, my strategies work at their best!
Like my analyses? don't forget to follow me, so you get updated when I post new ones. Also read my account and the 'status updates' to be informed.
Thank you for following and Succes with trading !
Richard from Rich.Exclusive.Trading