Libraries
Introduction
Pine Script® libraries are publications containing functions that can be reused in indicators, strategies, or in other libraries. They are useful to define frequently-used functions so their source code does not have to be included in every script where they are needed.
A library must be published (privately or publicly) before it can be used in another script. All libraries are published open-source. Public scripts can only use public libraries and they must be open-source. Private scripts or personal scripts saved in the Pine Script Editor can use public or private libraries. A library can use other libraries, or even previous versions of itself.
Library programmers should be familiar with Pine’s typing nomenclature, scopes, and user-defined functions. For more information, see the User Manual’s pages on the Type system and User-defined functions.
You can browse public library scripts in the Community Scripts feed.
Creating a library
A library is a special kind of script that begins with the library() declaration statement, rather than indicator() or strategy(). A library contains exportable function, method, UDT, and enum definitions, which constitute the only visible part of the library when imported by another script. Like other script types, libraries can also include Pine Script code in their global scopes. Programmers typically use a library’s global code to demonstrate how other scripts can use its exported structures.
A library script has a structure like the following, which must include one or more exportable functions or types:
Note that:
- The
//@description,//@enum,//@type,@field,// @function,// @param, and// @returnscompiler annotations are optional but we highly recommend you use them. These annotations document the library’s code and populate the default library description, which authors can use when publishing the library. - The export keyword is mandatory.
- <parameter_type> is mandatory, contrary to user-defined function parameter definitions in indicators or strategies, which are typeless.
- <script_code> can be any code one would normally use in an indicator, including inputs.
This is an example library:
Library functions
Exported functions and methods have slightly different requirements and constraints compared to non-exported functions.
In exported library function signatures (their first line):
- The export is mandatory.
- The function’s signature must include type keywords to specify the required type for each parameter.
- Programmers can include either the simple or series qualifier keywords to specify the qualified type that each parameter accepts. See the next section for more information.
Exported library functions have the following constraints:
- They cannot use variables from the library’s global scope except for those with the “const” qualifier, meaning they cannot use global variables initialized from script inputs, for example, or globally declared arrays.
- They cannot include calls to any
input.*()functions. - They can include
request.*()calls in their local scopes (if thedynamic_requestsparameter is not set tofalsein the library declaration statement), but theexpressionarguments of these calls cannot depend on any exported function parameters. See this section of the Other timeframes and data page to learn more about dynamic requests.
Library functions always return “simple” or “series” results. They do not return values with weaker qualifiers. Consequently, scripts cannot use their returned values in locations requiring “const” or “input” values. For example, a library function cannot calculate an argument for the show_last parameter in a plot() call because the parameter requires an “input int” or “const int” value.
Qualified type control
Pine Script automatically determines the qualified types of the arguments in calls to library functions based on how the functions use those arguments. If a parameter is compatible with the “series” type qualifier, its arguments automatically inherit that qualifier by default. Otherwise, Pine attempts to evaluate the argument with the “simple” qualifier. For example, consider the following exported function:
The length parameter of the ta.ema() function used in our function’s scope has the expected type “simple int”. The parameter can accept “simple int”, “const int” or “input int” values, but not “series int” values. Therefore, the Pine Script compiler automatically detects that the x parameter’s qualified type is “simple int”. This behavior explains why a call such as myCustomLibrary.myEma(x = 20) compiles successfully, but a call such as myCustomLibrary.myEma(x = bar_index) causes a compilation error. A literal value of 20 is of the type “const int”, meaning the script can convert it to a “simple int” argument. In contrast, bar_index has the type “series int”, and “series” arguments cannot inherit weaker qualifiers such as “simple”.
While library functions cannot return “const” or “input” values,
they can be written to produce “simple” results. This makes them
useful in more contexts than functions returning “series” results, as
some built-in functions do not allow “series” arguments. For example,
request.security()
requires a “simple string” argument for its symbol parameter when a script does not allow dynamic requests. If we wrote a
library function to assemble the argument to symbol in the following
way, the function’s result would not work with a non-dynamic request.*() call because it is of the “series
string” qualified type:
However, by restricting the parameter qualifiers to “simple”, we can force the function to yield a “simple” result. We can achieve this by prefixing the parameters’ type with the simple keyword:
Note that for the function to return a “simple” value, no “series” values can be used in its calculation; otherwise the result will be a “series” value.
One can also use the series keyword to prefix the type of a library function parameter. However, because library function parameters are qualified as “series” by default, using the keyword to specify the qualifier is often unnecessary.
User-defined types and objects
Libraries can export user-defined types (UDTs), and library functions can return the references (IDs) to objects of these types.
To export a UDT, prefix its definition with the export keyword, similar to exporting a function:
Another script can import this library to create objects of the point UDT. For example, the following script imports the hypothetical “Point” library published by the userName user, then uses the point.new() function to create a new point instance on each bar:
Note that:
- This example does not compile, because there is no “Point” library published by a
userNameuser. This example simply demonstrates how another script might use the hypothetical library. - This example script uses the alias
ptin the import statement. It then uses this alias as the namespace to access thepoint.new()function and thepointtype from our “Point” library. - The script uses
pt.pointas the type keyword for thenewPointvariable declaration. Using this keyword is optional, becausenewPointhas a defined reference. However, declaring the type explicitly using this keyword is required if we change the variable’s initial reference to na.
A library is required to export a UDT if any exported functions or methods accept or return references of that type or the IDs of collections that store references of the type. Likewise, a library must export a UDT if at least one field of another exported UDT uses the type.
By contrast, if a library uses objects of a UDT only for internal calculations, it does not need to export the type. For example, the following library uses the custom point type in its only exported function (drawPivots()). However, that function does not have a parameter of the point type, and it does not return a reference to any object of the type. Therefore, the point type does not require the export keyword in its declaration:
If the TradingView user published the above library, it could be used like this:
Enum types
Libraries can also export enum types, allowing other scripts to import sets of predefined, named constants that help control the values accepted by variables, conditional expressions, and collections.
For example, this library exports a State enum with three fields
representing distinct signal states: long, short, and neutral.
These fields represent the possible values a variable, expression, or
collection of the
enum type can take on:
A script that imports this library can use the members (values) of the
State enum as named states in its logic. Here, we show a simple,
hypothetical script that imports the “Signal” library published by the
userName user and uses the Signal.State enum to assign one of three
possible values to a mySignal variable:
Similar to exporting UDTs, a library must export an enum when its exported functions or methods accept or return the enum’s members, or when the fields of an exported UDT accept values of that enum type.
Publishing a library
Before you or other Pine Script programmers can reuse any library, it must be published. If you want to share your library with all TradingViewers, publish it publicly. To use it privately, use a private publication. As with indicators or strategies, the active chart when you publish a library will appear in both its widget (the small placeholder denoting libraries in the TradingView scripts stream) and script page (the page users see when they click on the widget).
Private libraries can be used in public Protected or Invite-only scripts.
After adding our example library to the chart and setting up a clean chart showing our library plots the way we want them, we use the Pine Editor’s “Publish Script” button. The “Publish Library” window comes up:
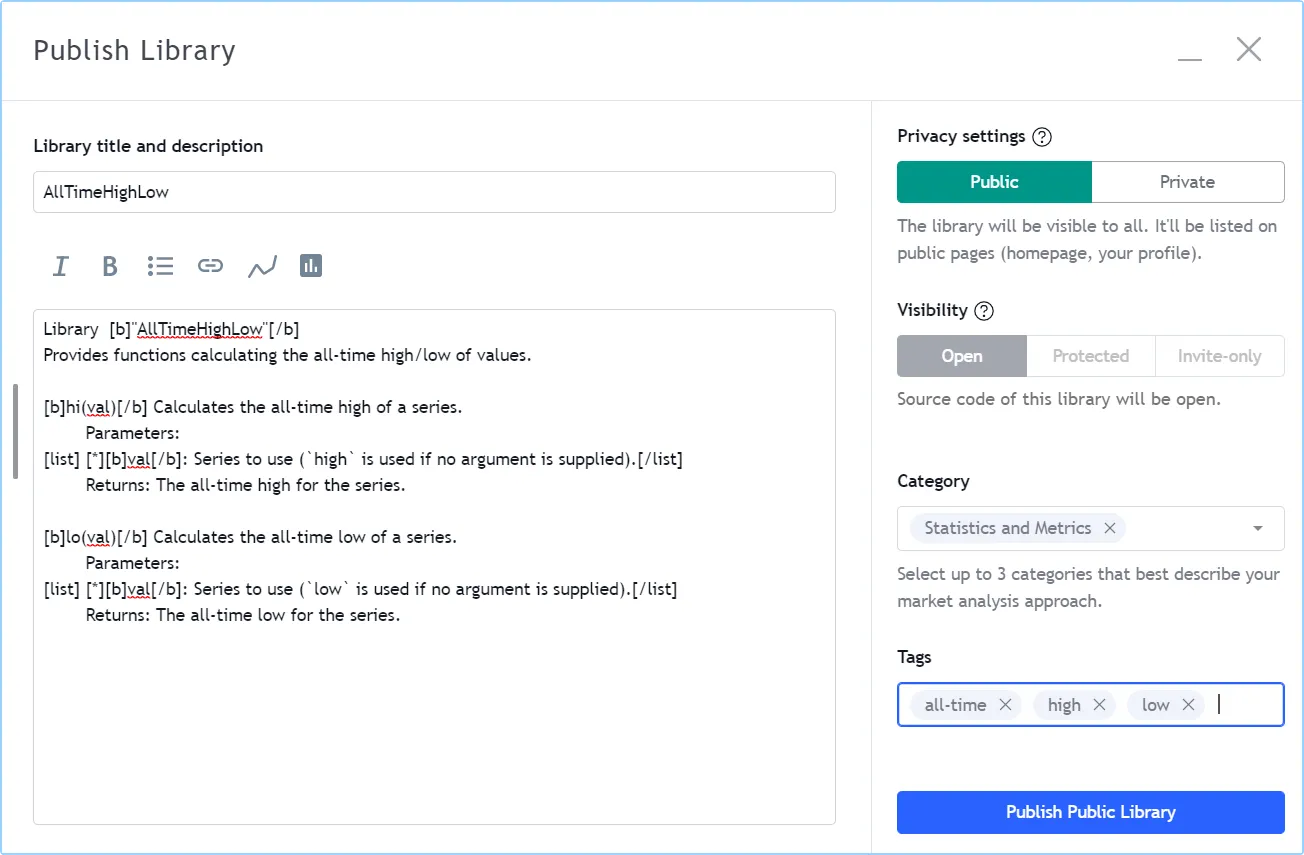
Note that:
- We leave the library’s title as is (the
titleargument in our library() declaration statement is used as the default). While you can change the publication’s title, it is preferable to keep its default value because thetitleargument is used to reference imported libraries in the import statement. It makes life easier for library users when your publication’s title matches the actual name of the library. - A default description is built from the compiler annotations we used in our library. We will publish the library wihout retouching it.
- We chose to publish our library publicly, so it will be visible to all TradingViewers.
- We do not have the possibility of selecting a visibility type other than “Open” because libraries are always open-source.
- The list of categories for libraries is different than for indicators and strategies. We have selected the “Statistics and Metrics” category.
- We have added some custom tags: “all-time”, “high” and “low”.
The intended users of public libraries being other Pine programmers; the better you explain and document your library’s functions, the more chances others will use them. Providing examples demonstrating how to use your library’s functions in your publication’s code will also help.
House Rules
Pine libraries are considered “public domain” code in our House Rules on Script Publishing, which entails that permission is not required from their author if you call their functions or reuse their code in your open-source scripts. However, if you intend to reuse code from a Pine Script library’s functions in a public protected or invite-only publication, explicit permission for reuse in that form is required from its author.
Whether using a library’s functions or reusing its code, you must credit the author in your publication’s description. It is also good form to credit in open-source comments.
Using a library
Using a library from another script (which can be an indicator, a strategy or another library), is done through the import statement:
import <username>/<libraryName>/<libraryVersion> [as <alias>]where:
- The <username>/<libraryName>/<libraryVersion> path will uniquely identify the library.
- The <libraryVersion> must be specified explicitly. To ensure the reliability of scripts using libraries, there is no way to automatically use the latest version of a library. Every time a library update is published by its author, the library’s version number increases. If you intend to use the latest version of the library, the <libraryVersion> value will require updating in the import statement.
- The
as <alias>part is optional. When used, it defines the namespace that will refer to the library’s functions. For example, if you import a library using theallTimealias as we do in the example below, you will refer to that library’s functions asallTime.<function_mame>(). When no alias is defined, the library’s name becomes its namespace.
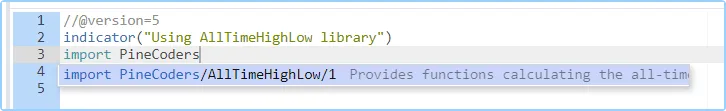
To use the library we published in the previous section, our next script will require an import statement:
As you type the user name of the library’s author, you can use the
Editor’s ctrl +
space / cmd “Auto-complete”
command to display a popup providing selections that match the available
libraries:
This is an indicator that reuses our library:
Note that:
- We have chosen to use the “allTime” alias for the library’s instance in our script. When typing that alias in the Editor, a popup will appear to help you select the particular function you want to use from the library.
- We use the library’s
hi()andlo()functions without an argument, so the default high and low built-in variables will be used for their series, respectively. - We use a second call to
allTime.hi(), but this time using close as its argument, to plot the highest close in the chart’s history.